Test Methods for analysis of Infusion panels (SOFIA)
Date
Brief overview
The SOFIA project studies the behavior of compression-stiffened curved panels, typical of the aerospace industry. The project's innovation lies in the manufacturing process of the stiffened panel, which uses resin infusion techniques instead of the conventional bonding (or co-bonding) of the stiffeners to the skin.
The project involves three entities: AICIA (University of Seville), ALESTIS, APPLUS, with the tasks assigned to each participant being those indicated below:
- AICIA (University of Seville) will carry out level 2 tests, of configuration details, to characterize the new admissible values of the different failure mechanisms of the panel.
- ALESTIS will perform numerical modeling of the tests and manufacture the necessary tooling. It is the project coordinator.
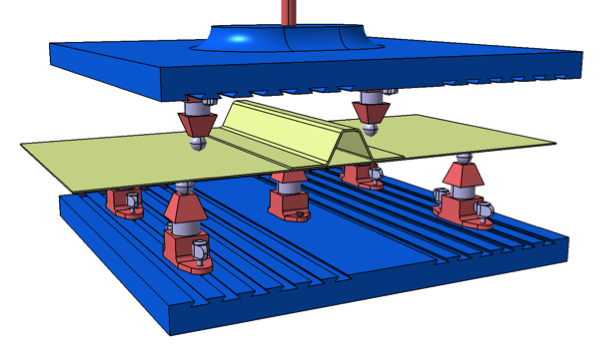
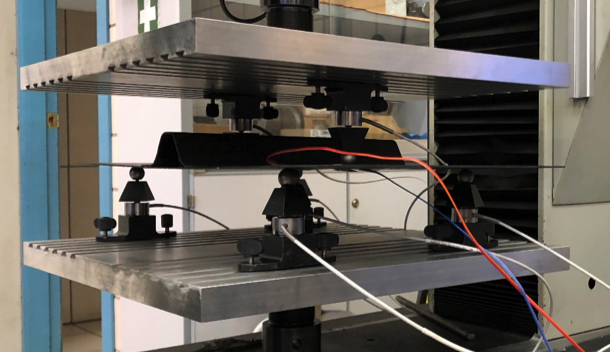
- APPLUS will perform the level 3 compression test of the entire panel.
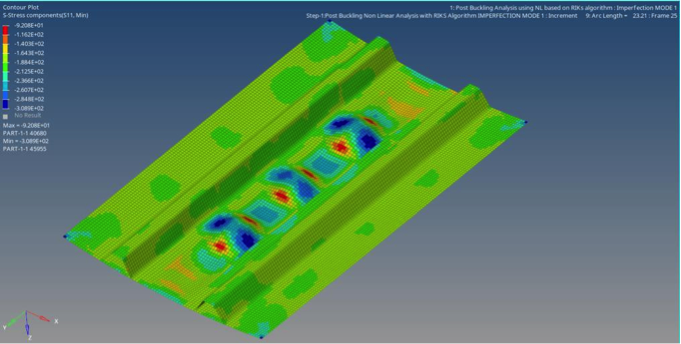
Sequentially, in the project, level 2 tests will be carried out to obtain certain admissible values for different failure mechanisms, and subsequently, a full panel compression test will be performed.
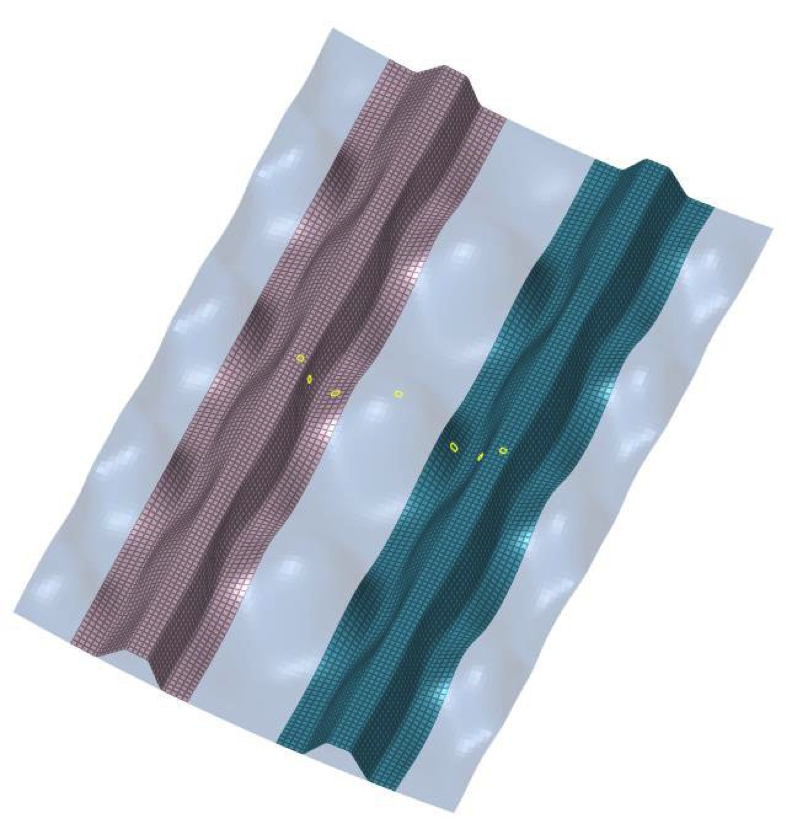
The admissible values obtained in the level 2 tests will be used, together with numerical modeling, to try to predict the panel failure during the level 3 test.
The trials that have been scheduled to take place include:
- GIC tests to determine the critical energy of the potential peel-off of the stiffener and the skin. Since the manufacturing process involves resin infusion, there is no adhesive interface between the two components from a formal point of view, therefore this permissible component is not preliminarily characterized.
- “Unfolding” tests , to determine the failure load at the stiffener's radii of agreement.
- Compression tests after impact , which allow for an acceptable compression strength in the panel with some damage (typically delamination), after suffering a normal impact to its surface.
- Seven-point bending tests , which allow (to some extent) the deformed configuration of the panel under compression and after suffering dents caused by the instability resulting from the compression.